



Next: MIAS Database
Up: False Positive Reduction
Previous: 2DPCA-Based False Positive Reduction
Contents
Evaluation of the False Positive Approaches
In this section, the results using the PCA and 2DPCA approaches
over a different set of manually selected RoIs are explained. The
evaluation is done by using the MIAS [169] and the
DDSM [67] databases and ROC analysis [120]. In
contrast to the previous chapters where this analysis was
performed counting pixel by pixel, we now proceed image by image,
i.e. dealing with all the image as a RoI with mass or as a RoI
with normal tissue (more details of this kind of evaluation are
given in Appendix ![[*]](file:/usr/share/latex2html/icons/crossref.png) ). To avoid confusions,
we will express the obtained
). To avoid confusions,
we will express the obtained 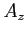 values using this image per
image strategy in the interval
values using this image per
image strategy in the interval ![$ [0-1]$](img704.png) , while when using the pixel
per pixel strategy the results will be given as a percentage.
, while when using the pixel
per pixel strategy the results will be given as a percentage.
In order to perform a more global evaluation of our results we
propose to compute the 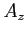 value for different ratios of number
of RoIs depicting masses and number of RoIs depicting normal
tissue (from ratio
value for different ratios of number
of RoIs depicting masses and number of RoIs depicting normal
tissue (from ratio 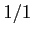 to ratio
to ratio 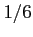 ). The idea of analyzing
these different ratios is twofold: firstly, to evaluate the
performance of our method on different levels of difficulty (a
ratio
). The idea of analyzing
these different ratios is twofold: firstly, to evaluate the
performance of our method on different levels of difficulty (a
ratio 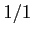 will obtain more optimistic results than
will obtain more optimistic results than 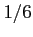 ), and
secondly, to compare our proposal with existing methods (the ones
presented in Table
), and
secondly, to compare our proposal with existing methods (the ones
presented in Table ![[*]](file:/usr/share/latex2html/icons/crossref.png) ). It is important to
notice that previous works only provide results for specific (and
usually different) ratios. Hence, analyzing all these ratios will
enable the comparison with them.
). It is important to
notice that previous works only provide results for specific (and
usually different) ratios. Hence, analyzing all these ratios will
enable the comparison with them.
Figure:
Performance of
the system using the MIAS database.
|
|
Subsections




Next: MIAS Database
Up: False Positive Reduction
Previous: 2DPCA-Based False Positive Reduction
Contents
Arnau Oliver
2008-06-17
![]() value for different ratios of number
of RoIs depicting masses and number of RoIs depicting normal
tissue (from ratio
value for different ratios of number
of RoIs depicting masses and number of RoIs depicting normal
tissue (from ratio ![]() to ratio
to ratio ![]() ). The idea of analyzing
these different ratios is twofold: firstly, to evaluate the
performance of our method on different levels of difficulty (a
ratio
). The idea of analyzing
these different ratios is twofold: firstly, to evaluate the
performance of our method on different levels of difficulty (a
ratio ![]() will obtain more optimistic results than
will obtain more optimistic results than ![]() ), and
secondly, to compare our proposal with existing methods (the ones
presented in Table
), and
secondly, to compare our proposal with existing methods (the ones
presented in Table ![]() ). It is important to
notice that previous works only provide results for specific (and
usually different) ratios. Hence, analyzing all these ratios will
enable the comparison with them.
). It is important to
notice that previous works only provide results for specific (and
usually different) ratios. Hence, analyzing all these ratios will
enable the comparison with them.