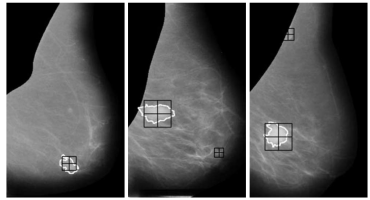
Mass detection
A breast mass is a localized swelling, protuberance, or lump in the breast, and is one of the clearest signs of breast cancer. Screening mammography is the most commonly used approach for detecting mammographic abnormalities, mainly because it allows detection at an early stage, a crucial issue for a high survival rate. However, it is well known that expert radiologists can miss a significant number of abnormalities. Typical reasons are that either the missed abnormality is located at the edge of glandular tissue, is obscured by overlying tissue, is only seen in one view or there is another distracting lesion visible elsewhere in the mammographic images.
We developed a supervised algorithm using contour and shape information for mass detection. We have designed a probabilistic template matching approach, where the template is generated from the analysis of the shapes of real masses. Once the detection has been completed, a set of suspicious ROIs are extracted from each mammogram, and subsequently classified by a false positive reduction algorithm as a ROI depicting a mass or a ROI depicting normal tissue. This false positive reduction step was based on the use of the two-dimensional principal components analysis algorithm.
In contrast with previous proposed algorithms for mass detection, we include in our experiments breast density information. The importance of this parameter is twofold. First, it is well known in mammography that breast density is highly correlated with the risk of developing breast cancer. And second, it has been proven that not only radiologists but also commercial CAD systems decrease their performance when detecting masses in dense breasts. Despite this fact, this parameter is usually not taken into account by these systems. In this work we will make use of breast density information in terms of the BIRADS standard.