Pre-processing steps
Some pre-processing steps.
- Peripheral enhancement
- Breast profile segmentation
In what follows we explain these steps
Peripheral enhancement
Digital mammograms may present an overexposed area in the peripheral part of the breast, which is visually shown as a darker area with lower contrast. This has a direct impact on image quality and affects image visualisation and assessment.
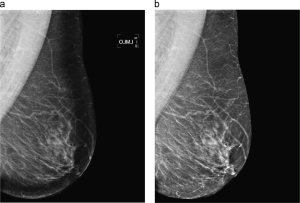
We proposed a method to enhance the overexposed peripheral breast area providing a more homogeneous and improved view of the whole mammogram. The method automatically restores the overexposed area by equalising the image using information from the intensity of non-overexposed neighbour pixels. The correction is based on a multiplicative model and on the computation of the distance map from the breast boundary.
In manual analysis, the proposed enhancement helps uncover different kind of abnormalities in the peripheral zone. Although expert radiologist may actually find them after thorough analysis of the mammogram, abnormalities are easier to detect after the enhancement. Moreover, the physical limits of the mass, which were not visible on the original mammograms, could properly be assessed after enhancement. On the other hand, automatic analysis, such as computer aided detection and breast density measurement systems can also profit from this enhancement.
Breast profile segmentation
The separation of the breast area from the backgrond and from the pectoral muscle is an important pre-processing step to achieve optimal breast parenchyma measurements, breast registration, or to put into focus a technique when we search for abnormalities.
Although this problem is usually solved by dividing it into two different segmentation strategies, one for the background and another one for the pectoral muscle, we tackled this problem jointly using a supervised single strategy. Namely, from a set of manually segmented mammograms, we model each of the three regions (breast, pectoral muscle, and background) using position, intensity, and texture information. Although the approach requires a training step, it allows a fast and reliable segmentation of new mammograms. The obtained results using 149 mammograms of the MIAS database show a high degree of overlap between manual and automatic segmentation.
We can provide the manual masks upon request.