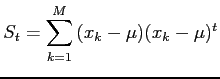 |
(4.1) |
The original eigenfaces approach of Turk and Pentland [180] for face recognition is based on the use of the Karhunen-Loeve transform in order to find the vectors that best account for the distribution of face images (forming the face subspace) within the entire image space. The total scatter matrix (the covariance matrix) is calculated as:
where
![]() is the mean
of all face samples and
is the mean
of all face samples and ![]() the number of face images represented
here by vector
the number of face images represented
here by vector ![]() . Using the Karhunen-Loeve transform it is
possible to obtain the subspace which maximizes:
. Using the Karhunen-Loeve transform it is
possible to obtain the subspace which maximizes:
where ![]() is a unitary column vector. With such
approach, the usefulness of the different eigenvectors to
characterize the variation among the images is ranked by the value
of the corresponding eigenvalue. Hence, it is possible to reduce
the dimensionality of the problem in only a few set of
eigenvectors, which are the so called eigenfaces. Thus, the
eigenfaces span the face subspace of the original image space, and
each face image can be transformed into this space by using them.
The result of this transformation is a vector of weights
describing the contribution of each eigenface in representing the
corresponding input image.
is a unitary column vector. With such
approach, the usefulness of the different eigenvectors to
characterize the variation among the images is ranked by the value
of the corresponding eigenvalue. Hence, it is possible to reduce
the dimensionality of the problem in only a few set of
eigenvectors, which are the so called eigenfaces. Thus, the
eigenfaces span the face subspace of the original image space, and
each face image can be transformed into this space by using them.
The result of this transformation is a vector of weights
describing the contribution of each eigenface in representing the
corresponding input image.
Furthermore, a model of each face is constructed by doing the above transformation for each face in the database. Thus, when a new face has to be tested, it will be classified as belonging to the most similar class. In the original algorithm, this similarity is calculated using the Nearest Neighbour algorithm [180].